Modeling diffusive alpha-particle radiation therapy
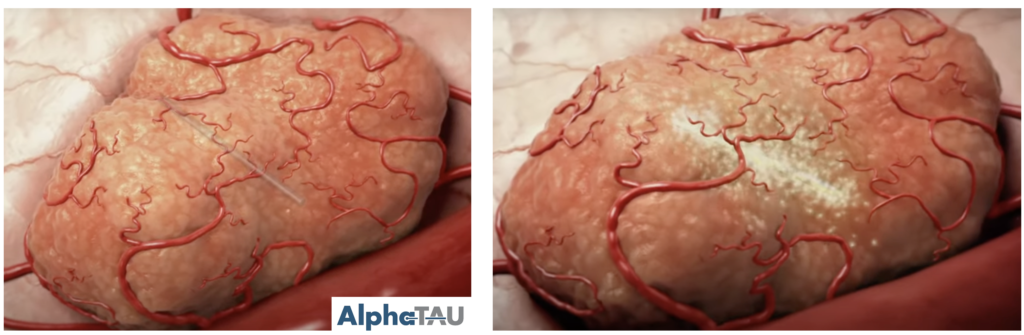
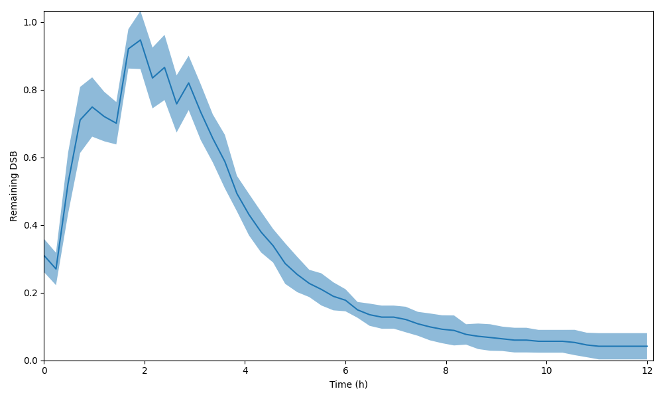
Simulating the diffusion of alpha-particle emitters in decay chains, such as Ra224, using the TOPAS toolkit is crucial for understanding the underlying mechanisms of diffusive alpha radiotherapy (DART). This process can result in daughter particles, like Pb-212, traveling millimeters away from the initial source, impacting the distribution of radiation dose. Accurate Monte Carlo-based dose calculations […]
Modeling diffusive alpha-particle radiation therapy Read More »